What is the macula?
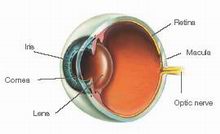 The macula is a small, specialized area in the middle of the retina, where light is centrally-focused onto inside our eyes. This central vision is the vision we use for reading, driving, recognising faces, threading needles and other fine detailed work.
The macula is a small, specialized area in the middle of the retina, where light is centrally-focused onto inside our eyes. This central vision is the vision we use for reading, driving, recognising faces, threading needles and other fine detailed work.
What is Age-related Macular Degeneration?
Macular degeneration happens when the macula suffers thinning, atrophy, and in some cases bleeding. Age-related Macular Degeneration, or AMD, is the leading cause of vision loss in the western world, and typically affects people over 60 years of age.
The most common form of the disease is known as Dry AMD, which occurs in approximately 80 to 90% of people with AMD. In Dry AMD the vision loss is usually very gradual and is seldom severe. Areas of the central retina gradually become thin and stop working and some sufferers notice blank areas in their vision.
Some people develop a more aggressive form of the disease called Wet AMD that can lead to rapid and severe vision loss. In Wet AMD, abnormal blood vessels grow under the macula and eventually leak fluid, bleed or lift up the retina. The longer these abnormal new vessels continue to leak, bleed and grow, the more central vision will be lost.
Left untreated, these fragile vessels will cause scarring and irreversible loss of the detailed central vision. Sometimes only one eye loses vision while the other eye continues to see well for many years. If both eyes are affected however, reading and close-up work may become extremely difficult. With AMD, the eye still sees objects to the side since peripheral vision is not affected.
What are the symptoms of AMD?
Most patients with AMD will notice difficulty in reading as words become blurred or crowded. There may be a black or grey spot in your central vision. A frequent and important early symptom of Wet AMD is distortion when straight lines appear bent or wavy. These changes in eyesight are important symptoms and if they occur you should contact an ophthalmologist promptly. 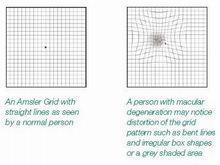
The Amsler Grid Test is a simple and effective way to test the health of your macula. It is a pattern of intersecting lines with a black dot in the middle. The central black dot is used as a focal point. With normal vision, all lines surrounding the black dot will look straight and evenly-spaced with no missing or odd looking areas. When there is disease affecting the macula such as macular degeneration, the lines can look bent, distorted and/or missing.
How is AMD diagnosed?
If Wet AMD is suspected, special tests such as optical coherence tomography (OCT) and fluorescein angiography are usually required. OCT is a non-contact method of scanning the macula to look for fluid leaks, the first sign of Wet AMD. Fluorescein angiography is used to locate exactly where the leaking blood vessels are. In this test, dye is injected in the body, and with a special camera a series of photographs are taken as the dye passes through the retina, putting together a map of the problem which can be used by the doctor during treatment.
Many people do not realize they have macular problems until blurred vision becomes obvious. An eye specialist can examine the macula and identify early changes.
How can it be treated?
Various measures have been shown to decrease chances of the disease getting worse. These include vitamin supplementation, quitting smoking, and dietary changes such as eating less fatty foods such as red meat and dairy products. Certain foods also seem to protect against the development of Wet AMD such as fish oils and nuts.
With Wet AMD, several different treatments are possible:
• Avastin and Lucentis Injections
These are injected into the eye, and may need to be repeated several times over the course of several months. They have been shown to improve vision in people with Wet AMD, so long as scarring has not started to take place. This is the only treatment which seems to improve vision; other treatments are preventive measures to stall the development of AMD.
• Thermal Laser Therapy (Photocoagulation)
In this procedure, the heat from a laser light is used to cauterize the abnormal leaky blood vessels. However, this treatment also damages overlying normal retina.
• Photodynamic Therapy (PDT)
PDT uses a light-activated drug (Visudyne) and a special non-thermal laser to selectively destroy abnormal blood vessels while preserving surrounding normal healthy tissue.
What if I have AMD?
If you have AMD you are advised:
1. If you smoke, to stop
2. Take regular Omega-3- fatty acids which are found in fish
3. Take the antioxidants lutein and zeozanthin which are found in green leafy vegetables.
The above steps will reduce the progression of AMD if you already have it.
Advanced macular degeneration can rob a patient of the ability to drive, read or even see faces. However as peripheral vision remains, AMD sufferers can usually take basic care of themselves.
Early detection and treatment can help tremendously. If you think you suffer from AMD or any form of macular degeneration, consult a qualified ophthalmologist or eye specialist for advice.







Join the Discussion
Type out your comment here:
You must be logged in to post a comment.